Current U.S. Mortgage Rates and Market Trends
Keep up with the most recent U.S. mortgage rates and investigate the implications of market developments for both potential investors and homebuyers.
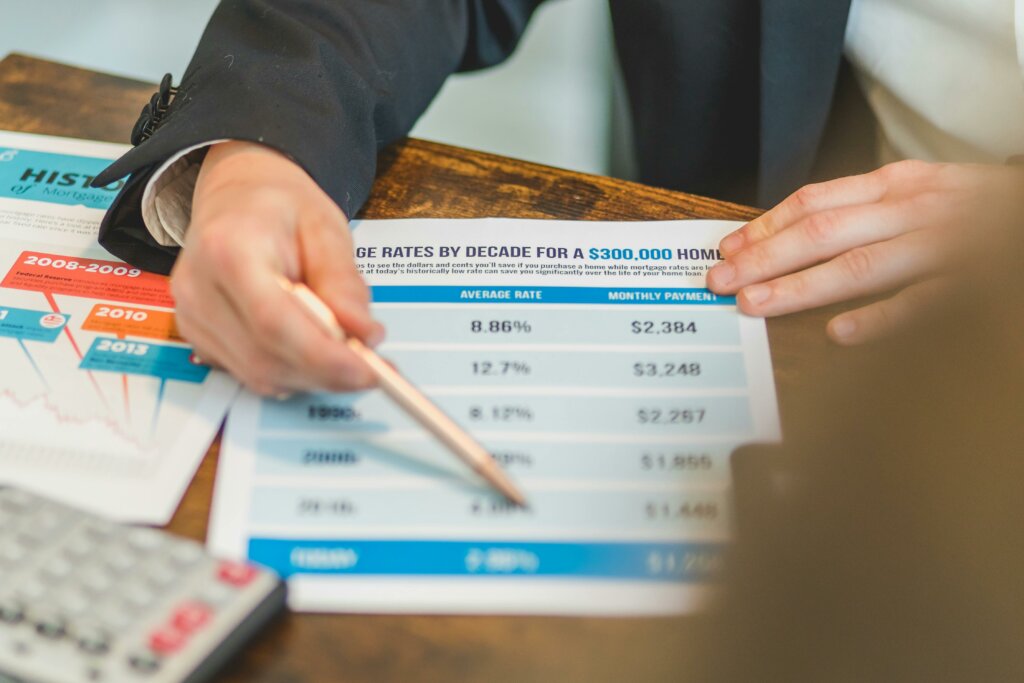
As the market is influenced by economic conditions and Federal Reserve policy, mortgage rates in the United States have been volatile lately. Millions of Americans are affected by these changes, including real estate investors, long-time homeowners, and first-time purchasers. Understanding the current patterns and variables influencing rates will help you make informed financial decisions, whether you’re wanting to buy, refinance, or comprehend the housing market as a whole. This essay will analyze current trends in mortgage rates, the factors influencing them, and the potential implications for borrowers nationwide.
What Affects Current Mortgage Rates?
Anyone navigating the home market needs to understand why mortgage rates change. The Federal Reserve’s policies, the overall financial environment, and economic data have the most effects on rates. For example, inflation has a significant impact since rising inflation raises interest rates, especially mortgage interest rates. Mortgage rates have increased as a result of the Federal Reserve’s recent rate hikes to combat inflation. Since a strong economy tends to drive up mortgage rates, employment trends and GDP growth also have an effect on rates. On the other hand, the Fed may cut rates to encourage borrowing during economic downturns, which could result in more inexpensive mortgages.
Stable Fixed-Rate Mortgages in a Changing Market
Because they provide consistent payments throughout time, regardless of changes in market rates, fixed-rate mortgages (FRMs) continue to be a popular option. Homeowners will not have to worry about rising rates thanks to this stability, but they may also miss out on rate reductions unless they refinance. Compared to prior years when rates were historically low, fixed-rate mortgages are currently trending at roughly 6-7% for a 30-year loan. These rates offer long-term security even though they could seem high to someone used to lower figures. In the face of a shifting financial environment, FRMs can provide predictability for people who are determined to remain in one residence for many years.
Adjustable-rate mortgages are a flexible option, but they come with a higher risk
Another choice is an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), where rates fluctuate over time in response to market conditions. These loans are appealing to people who anticipate a drop in interest rates or who want to sell or refinance in the coming years because they often provide lower initial rates than fixed-rate mortgages. However, there is some danger associated with ARMs given the present trend of rising interest rates. Monthly payments for ARMs can rise sharply as interest rates rise, which could surprise borrowers. Despite this, ARMs are still a good choice for people looking for short-term flexibility and cheaper upfront costs, but in the current market, they should be handled carefully.
Amid Increasing Rates, Refinancing Options
As interest rates climb, refinancing has lost appeal to existing homeowners. Homeowners may now have to pay higher rates than their initial mortgage terms, when before low mortgage rates promoted refinancing. Nonetheless, people who want to shorten their loan term, access cash, or consolidate debt may still find that refinancing makes sense. Cash-out refinances are popular among homeowners who want to use their home equity to finance major purchases or investments. The alternative is still advantageous for some financial objectives even though refinancing activity has decreased. Borrowers must, however, assess the long-term effects, taking closing expenses and other fees into account that may have an impact on total savings.
Prospects for the Housing Market and Buyer Demand
The demand for property has also been impacted by the present mortgage rate environment, especially among first-time purchasers who are having financial difficulties. Increased monthly payments due to rising rates may cause prospective buyers to postpone purchases or look at less expensive options, including smaller homes or properties in less competitive markets. Due to a continuing housing shortage and demographic reasons, demand for homes is relatively stable despite increased rates. Competitive purchasing activity is still there in cities with robust job markets, but purchasers are growing more astute, looking for price breaks and negotiating closing costs to balance high mortgage prices.
Understanding the market’s impacting elements and accessible options is essential for navigating the U.S. mortgage landscape in 2024. Depending on personal requirements and market conditions, each mortgage type has unique benefits, ranging from fixed-rate stability to the flexibility (and hazards) of adjustable rate mortgages. Today’s homeowners and buyers must make decisions based on long-term affordability and possible savings because rates are still high. Even though the current environment presents difficulties, understanding the factors influencing these rate changes can enable borrowers to make wise choices and confidently enter the real estate market.







